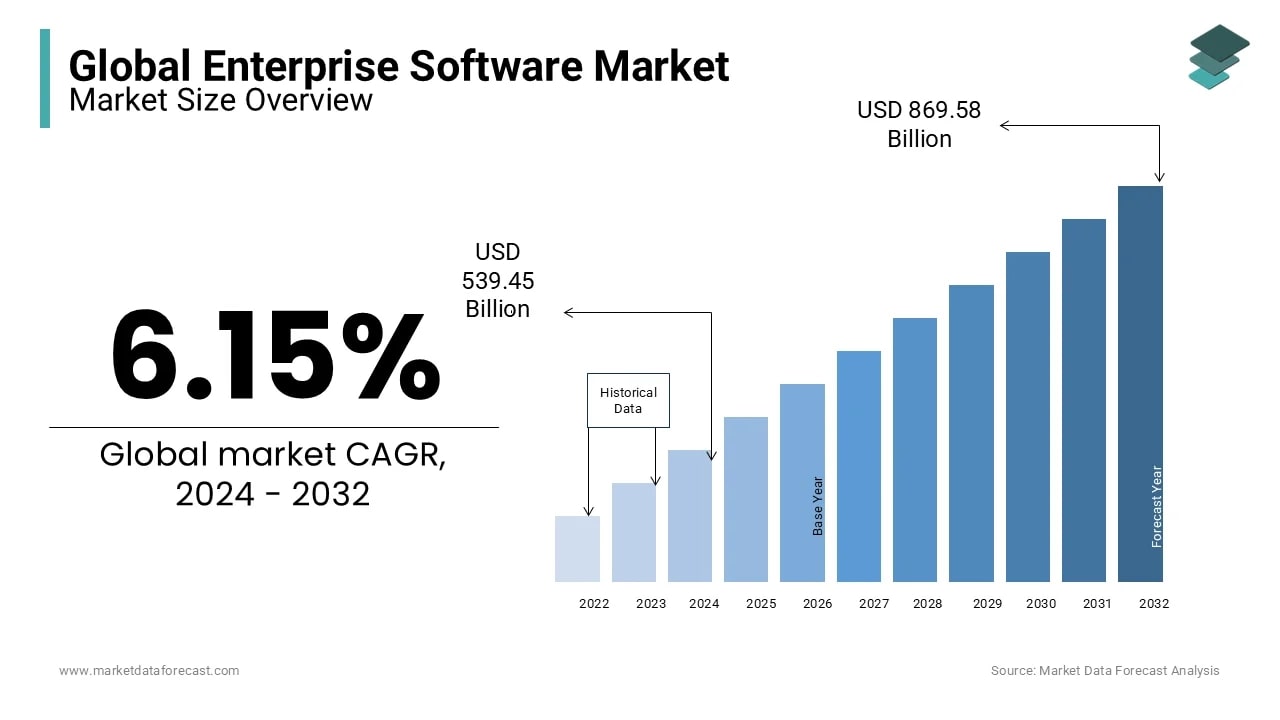
Enterprise software plays a crucial role in helping companies and business organizations streamline operations, enhance efficiency, and maintain a competitive edge. From managing resources to enhancing customer relationships, enterprise software applications encompass a range of tools that support essential business functions. Recent projections indicate that the global enterprise software market is expected to reach approximately USD 539.45 billion in 2024, with forecasts suggesting a growth of USD 869.58 billion by the year 2032, reflecting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.15% during this period. By integrating various types of enterprise software into their operations, businesses can automate repetitive tasks, make data-driven decisions, and ultimately achieve higher productivity.
This guide explores the key types of enterprise software that drive business success, including Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP), Customer Relationship Management (CRM), and Business Intelligence (BI). We’ll break down each software type, its unique features, and benefits, and provide real-world examples of how organizations implement these tools to solve critical business challenges.
Whether you’re evaluating new software solutions or seeking to understand the evolving landscape of business software applications, this comprehensive guide offers insights into the tools shaping the future of business. Let’s dive into the core types of enterprise software and discover how they can propel your business forward.
Table of Contents
- Types of Enterprise Software
- Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
- Supply Chain Management (SCM)
- Human Resource Management (HRM)
- Business Intelligence (BI)
- Content Management System (CMS)
- Marketing Automation
- Project Management Software
- Business Process Management (BPM)
- Enterprise Content Management (ECM)
- Customer Service Software
- Accounting and Finance Software
- Enterprise Asset Management (EAM)
- Collaboration Tools
- Procurement Software
- A Quick Comparison of Enterprise Software Types
- FAQs on Enterprise Software
- What are the benefits of using enterprise software?
- How do I choose the right type of enterprise software for my business?
- What is the difference between ERP and CRM software?
- Can small businesses benefit from enterprise software?
- How does cloud-based enterprise software differ from on-premises software?
- What role does AI play in enterprise software?
- Are there security risks associated with enterprise software?
- How can enterprise software improve customer service?
- What are the typical costs involved in implementing enterprise software?
- What is the expected lifespan of an enterprise software solution?
- Conclusion
Types of Enterprise Software
Implementing various types of enterprise software is essential for modern businesses to enhance productivity, streamline operations, and facilitate better decision-making. Each enterprise software solution serves a unique function, from managing resources to improving customer relationships, making them indispensable in today’s competitive business landscape. Below are some key enterprise software applications that businesses commonly use.
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)
What is Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)?
ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) software integrates core business processes into a centralized system, allowing departments like finance, inventory, and human resources to share information efficiently. By consolidating data from various functions, ERP improves workflow accuracy and visibility, helping businesses make faster, more informed decisions and streamline operations.
Key Features of Enterprise Resource Planning software
- Financial management and reporting
- Inventory and supply chain management
- Human resource and payroll management
- Order processing and procurement
- Real-time data access and analytics
Benefits of ERP systems
ERP software enhances business efficiency by centralizing data, automating routine tasks, and reducing operational costs. The real-time access to information aids in informed decision-making and enables better resource management.
Use Case Example of Enterprise Resource Planning software
A global manufacturing firm implemented ERP software to synchronize its supply chain and production processes. This integration reduced lead times by 30% and improved inventory accuracy, leading to lower costs and faster order fulfillment.
Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
What is Customer Relationship Management (CRM)?
CRM (Customer Relationship Management) software centralizes customer data, enabling businesses to manage customer interactions, track sales, and analyze customer behavior. This tool is essential for building and maintaining strong customer relationships, as it allows businesses to personalize communication and better understand customer needs, ultimately enhancing customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Key Features of Customer Relationship Management software
- Contact management and segmentation
- Sales pipeline tracking and management
- Customer support and case management
- Marketing automation
- Analytics and Reporting
Benefits of CRM system
By centralizing customer data, CRM software provides insights into customer behaviors and preferences, which enables personalized communication and improves customer satisfaction and retention.
Use Case Example of CRM software
A retail company used CRM software to track customer purchases and preferences, enabling targeted promotions. This approach led to a 25% increase in repeat customers within six months.
Supply Chain Management (SCM)
What is Supply Chain Management (SCM)?
SCM (Supply Chain Management) software manages the flow of goods, information, and finances across the supply chain, from procurement to delivery. By tracking inventory levels, demand forecasting, and logistics, SCM software enables businesses to optimize their supply chain processes, reduce costs, and respond more effectively to market demands.
Key Features of Supply Chain Management Software
- Demand forecasting and planning
- Supplier and vendor management
- Inventory tracking and optimization
- Logistics and transportation management
- Real-time tracking and analytics
Benefits of SCM software solution
SCM software improves supply chain transparency, reduces excess inventory, and lowers costs by optimizing each stage of the supply chain. It enables businesses to respond swiftly to market demands and manage supplier relationships more effectively.
Use Case Example of Supply Chain Management software
A large e-commerce company adopted SCM software to streamline its inventory and logistics processes. As a result, it reduced stockouts by 20% and lowered logistics costs by 15%, improving overall customer satisfaction.
Human Resource Management (HRM)
What is Human Resource Management (HRM)?
HRM (Human Resource Management) software streamlines employee management processes, including hiring, payroll, and performance evaluations. This software centralizes employee data, allowing HR teams to efficiently manage records, track employee growth, and maintain regulatory compliance, while also fostering a positive work environment and supporting workforce development.
Key Features of Human Resource Management Software
- Employee information management
- Recruitment and applicant tracking
- Payroll processing and benefits administration
- Performance and talent management
- Training and development tracking
Benefits of HRM system
HRM software simplifies employee management processes, improves compliance with regulations, and enhances employee engagement through better performance tracking and development opportunities.
Use Case Example of Human Resource Management Software
A mid-sized tech company used HRM software to automate payroll and manage employee records. This system saved the HR team 20 hours per month in administrative tasks, allowing them to focus on talent development.
Business Intelligence (BI)
What is Business Intelligence (BI)?
BI (Business Intelligence) software collects and analyzes business data, transforming it into actionable insights through data visualization, reports, and trend analysis. By leveraging BI tools, organizations gain a deeper understanding of their performance, market trends, and operational inefficiencies, empowering leaders to make data-driven decisions that enhance competitiveness and profitability.
Key Features of Business Intelligence Software
- Data collection and integration from multiple sources
- Dashboard and data visualization tools
- Ad-hoc and scheduled reporting
- Predictive analytics and trend forecasting
- Data warehousing
Benefits of BI system
BI software provides insights into business performance, enabling data-driven decisions that can improve productivity, profitability, and market competitiveness. It helps identify trends and patterns that may not be visible otherwise.
Use Case Example of Business Intelligence software
A retail chain used BI software to analyze sales patterns and adjust inventory based on regional demand, resulting in a 15% increase in sales in high-demand locations.
Content Management System (CMS)
What is a Content Management System (CMS)?
CMS (Content Management System) software enables businesses to create, manage, and publish digital content on websites without needing extensive coding skills. This tool is crucial for enterprises that rely on frequent content updates, as it allows teams to keep information relevant and accurate, enhancing user experience and search engine visibility.
Key Features of Content Management System Software
- Content creation and editing tools
- Media library for images and documents
- User role permissions and access controls
- SEO optimization tools
- Version control and publishing workflows
Benefits of CMS solution
CMS software simplifies content creation and management, making it easy for non-technical users to maintain a website. It also enables businesses to keep content fresh and relevant, enhancing user engagement.
Use Case Example of Content Management System
A healthcare provider used CMS software to update its website with health tips and resources for patients, resulting in a 30% increase in site visits and improved patient engagement.
Marketing Automation
What is Marketing Automation?
Marketing Automation software automates repetitive marketing tasks like email campaigns, social media posting, and customer segmentation. By allowing businesses to deliver personalized messages and track campaign performance, this software helps improve targeting and engagement, resulting in higher conversion rates and streamlined marketing operations.
Key Features of Marketing Automation Software
- Campaign management and tracking
- Customer segmentation and targeting
- Email marketing automation
- Lead scoring and nurturing
- Analytics and performance tracking
Benefits of Marketing Automation Solutions
Marketing automation increases efficiency by reducing manual marketing tasks and allows businesses to target the right audiences at the right time, leading to higher conversion rates.
Use Case Example Marketing Automation
A B2B company adopted marketing automation to segment its leads and nurture them with targeted email campaigns. This resulted in a 40% increase in lead-to-customer conversions.
Project Management Software
What is Project Management Software (PMS)?
Project Management software organizes and oversees project tasks, timelines, and resources, ensuring projects are delivered on time and within budget. By tracking progress and facilitating collaboration, this tool keeps teams aligned on goals and improves project outcomes, making it essential for organizations managing complex or cross-functional projects.
Key Features of Project Management Software
- Task assignment and tracking
- Project timelines and Gantt charts
- Budgeting and resource allocation
- Collaboration tools and document sharing
- Reporting and analytics
Benefits of Project Management Software Solution:
The project management software tool enhances team collaboration, optimizes resource use, and improves project delivery by keeping everyone on the same page and ensuring accountability.
Use Case Example of Project Management Software
A construction company used project management software to manage complex project timelines and resources, resulting in a 25% reduction in project delays.
Business Process Management (BPM)
What is Business Process Management (BPM)?
BPM (Business Process Management) software models, automates, and optimizes business workflows, helping organizations increase efficiency and adaptability. By automating repetitive tasks and tracking process performance, BPM enables businesses to improve productivity, reduce errors, and respond quickly to changing demands.
Key Features of Business Process Management Software
- Workflow automation and tracking
- Process modeling and visualization
- Integration with existing systems
- Reporting and performance metrics
- Compliance tracking
Benefits of BPM system
BPM software improves operational efficiency by automating repetitive tasks and streamlining business processes, which reduces errors and speeds up workflows.
Use Case Example of Business Process Management Software
A logistics company implemented BPM software to optimize its shipping processes, reducing processing time by 20% and improving customer satisfaction.
Enterprise Content Management (ECM)
What is Enterprise Content Management (ECM)?
ECM (Enterprise Content Management) software manages an organization’s documents, records, and digital assets, making it easier to store, retrieve, and secure information. ECM solutions help businesses comply with regulatory requirements by providing controlled access to critical files. By organizing content efficiently, ECM improves productivity and ensures that employees can access up-to-date information when they need it.
Key Features of Enterprise Content Management Software
- Document management and version control
- Digital asset management and storage
- Role-based access control and permissions
- Compliance and regulatory support
- Search and retrieval functions
Benefits of ECM system
ECM software reduces paperwork, enhances document security, and ensures compliance, making it easier for businesses to manage large volumes of information. It improves collaboration and speeds up decision-making by providing quick access to important documents.
Use Case Example of Enterprise Content Management
A legal firm implemented ECM to manage case files and documents. This system reduced retrieval time by 40% and ensured compliance with industry regulations.
Customer Service Software
What is Customer Service Software?
Customer Service Software helps businesses manage and resolve customer inquiries efficiently, providing tools to handle support tickets, live chats, and knowledge bases. This software enables companies to improve customer satisfaction by reducing response times and delivering consistent support. By centralizing customer interactions, customer service software ensures that issues are resolved efficiently and accurately.
Key Features of Customer Service Software
- Ticket management and prioritization
- Live chat and multichannel support
- Knowledge base and FAQ management
- Customer feedback collection
- Analytics and reporting tools
Benefits of Customer Service Software
This software enhances customer satisfaction by streamlining support workflows, reducing response times, and improving the quality of assistance. It also provides valuable insights into customer needs and common issues.
Use Case Example of Customer Service Software
An online retailer implemented customer service software to handle support tickets and live chat. This improved the team’s response time by 30% and increased customer satisfaction ratings.
Accounting and Finance Software
What is Accounting and Finance Software?
Accounting and Finance Software manages a business’s financial transactions, including accounting, budgeting, and payroll, ensuring accurate financial oversight. This software provides tools for tracking revenue, expenses, and cash flow, which are critical for informed decision-making. By automating financial tasks, accounting software helps maintain compliance with financial regulations and reduces the risk of errors.
Key Features of Accounting and Finance Software
- Accounts payable and receivable
- Budgeting and forecasting
- Payroll processing and tax management
- Financial reporting and analysis
- Compliance and audit support
Benefits of Accounting and Finance Software
It improves financial accuracy, simplifies budgeting, and ensures regulatory compliance, allowing businesses to gain a clear picture of their financial health.
Use Case Example of Accounting and Finance Software
A small business used accounting software to automate payroll and track expenses, saving 15 hours per month in administrative tasks and improving financial accuracy.
Enterprise Asset Management (EAM)
What is Enterprise Asset Management (EAM)?
EAM (Enterprise Asset Management) software oversees the maintenance and lifecycle of physical assets, such as machinery, equipment, and buildings, to maximize efficiency and reduce downtime. This software helps businesses track asset performance, schedule maintenance, and predict asset failures before they occur. EAM solution enables companies to extend asset lifespan and manage their investments more effectively.
Key Features of Enterprise Asset Management software
- Asset tracking and inventory management
- Preventive and predictive maintenance scheduling
- Work order management
- Compliance and risk management
- Analytics and reporting on asset performance
Benefits of EAM system
EAM software reduces operational costs by optimizing asset maintenance and extending asset life. It minimizes downtime and helps prevent unexpected breakdowns, which are costly for businesses.
Use Case Example of Enterprise Asset Management software
A utility company used EAM software to manage its equipment maintenance, which resulted in a 25% reduction in maintenance costs and increased asset availability.
Collaboration Tools
What are Collaboration Tools?
Collaboration Tools facilitate teamwork by enabling real-time communication, file sharing, and project collaboration among employees, regardless of location. These tools are essential for remote and hybrid teams, allowing software development team members to work together effectively on shared projects. Collaboration tools keep everyone connected and ensure that teams can access and edit documents, track project status, and communicate seamlessly.
Key Features of Collaboration Software
- Messaging and video conferencing
- Shared workspaces and file sharing
- Task assignment and project tracking
- Document version control
- Integration with other productivity tools
Benefits of Collaboration Tools
These tools enhance productivity by improving communication, reducing email clutter, and allowing software development teams to coordinate more effectively, particularly in remote settings.
Use Case Example of Collaboration Software
A global tech company adopted collaboration tools to facilitate communication among its remote teams, resulting in a 20% increase in productivity.
Procurement Software
What is Procurement Software?
Procurement Software streamlines purchasing and supplier management processes, helping businesses manage contracts, track spending, and ensure compliance. This software simplifies the procurement cycle from purchase requisition to order fulfillment, improving supplier relationships and controlling costs. Procurement software also provides insights into purchasing trends, enabling businesses to negotiate better terms with suppliers.
Key Features of Procurement software
- Supplier management and evaluation
- Purchase order processing
- Contract management and renewals
- Spend analysis and reporting
- Compliance and audit support
Benefits of Procurement Software
Procurement software helps reduce costs, improves supplier management, and ensures compliance with procurement policies. It also provides greater transparency into spending, helping businesses make informed purchasing decisions.
Use Case Example of Procurement software
A manufacturing firm implemented procurement software to manage its suppliers and track spending, leading to a 15% reduction in procurement costs and improved supplier relationships.
A Quick Comparison of Enterprise Software Types
To help you evaluate the types of enterprise software best suited to your business needs, here’s a comparison of key software types based on features, benefits, and ideal use cases. This table gives an at-a-glance view, making it easy to identify the right business software applications for various organizational functions.
| Enterprise Software Type | Key Features | Benefits | Ideal Use Cases |
|---|---|---|---|
| Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) | Centralized data management, inventory tracking, financial reporting, HR management | Streamlines workflows, improves data accuracy, reduces costs | Suitable for companies needing integrated management of multiple functions, especially in manufacturing and retail |
| Customer Relationship Management (CRM) | Contact management, sales pipeline tracking, customer support tools, marketing automation | Enhances customer relationships, increases sales, improves retention | Ideal for businesses focused on sales and customer service, such as retail, e-commerce, and B2B firms |
| Supply Chain Management (SCM) | Demand forecasting, inventory tracking, supplier management, logistics optimization | Increases supply chain transparency, reduces inventory costs, enhances logistics | Useful for businesses with complex supply chains, including e-commerce, manufacturing, and retail |
| Human Resource Management (HRM) | Employee data management, payroll, recruitment, performance tracking | Simplifies HR processes, ensures compliance, boosts employee engagement | Beneficial for companies with large or growing teams in need of efficient HR management |
| Business Intelligence (BI) | Data collection, dashboard visualization, trend forecasting, reporting tools | Enables data-driven decisions, identifies trends, improves profitability | Ideal for data-focused organizations that require detailed analytics, such as finance, marketing, and operations |
| Content Management System (CMS) | Content creation tools, media library, access controls, SEO tools | Simplifies website management, enhances user experience, boosts SEO | Best suited for businesses that frequently update their websites, like media, healthcare, and retail |
| Marketing Automation | Campaign management, customer segmentation, email automation, lead nurturing | Saves time, improves targeting, boosts conversion rates | Valuable for marketing teams in B2B and B2C sectors needing automated, targeted campaigns |
| Project Management Software | Task assignment, project timelines, resource allocation, collaboration tools | Enhances collaboration, optimizes resource use, ensures timely project completion | Ideal for teams handling complex or cross-functional projects, common in tech, construction, and engineering |
| Business Process Management (BPM) | Workflow automation, process modeling, integration, compliance tracking | Streamlines operations, increases productivity, adapts to business changes | Beneficial for organizations focused on efficiency and process improvement |
| Enterprise Content Management (ECM) | Document management, digital asset storage, compliance support | Enhances document access, supports regulatory compliance, improves collaboration | Suitable for industries with high documentation needs, like legal, healthcare, and finance |
| Customer Service Software | Ticket management, live chat, knowledge base, customer feedback tools | Improves response times, enhances customer satisfaction, centralizes support | Essential for companies with a customer support focus, such as retail, tech, and e-commerce |
| Accounting and Finance Software | Accounts management, budgeting, payroll, tax compliance | Ensures financial accuracy, simplifies budgeting, maintains compliance | Ideal for businesses that require efficient financial management, common in all industries |
| Enterprise Asset Management (EAM) | Asset tracking, maintenance scheduling, risk management | Reduces maintenance costs, improves asset utilization, minimizes downtime | Perfect for asset-heavy industries, like manufacturing, utilities, and infrastructure |
| Collaboration Tools | Messaging, file sharing, video conferencing, project tracking | Enhances team communication, improves productivity, supports remote work | Beneficial for remote and hybrid teams across all industries |
| Procurement Software | Supplier management, purchase order processing, spend analysis | Reduces procurement costs, improves supplier relations, increases transparency | Best for companies with significant purchasing needs, common in manufacturing and retail |
FAQs on Enterprise Software
Get quick answers to common questions about enterprise software, covering key benefits, selection tips, and security considerations to help you choose the best software solutions for your business.
What are the benefits of using enterprise software?
Enterprise software provides numerous advantages, including improved efficiency, data centralization, and scalability. By automating processes and integrating different functions (such as finance, HR, and supply chain), enterprise software reduces manual tasks, minimizes errors, and enables real-time data sharing across departments. This leads to faster decision-making, cost savings, and better alignment with organizational goals.
How do I choose the right type of enterprise software for my business?
Selecting the right enterprise software solution depends on your business’s specific needs, size, and industry. Start by identifying key pain points or areas needing improvement, such as customer relationship management, resource planning, or project management. Research software options that specialize in those areas, review their features and evaluate user reviews. It’s also essential to consider scalability, integration capabilities with your current systems, and support from a reliable vendor.
What is the difference between ERP and CRM software?
ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) software is designed to centralize and streamline internal business processes across departments, covering finance, inventory, and HR. CRM (Customer Relationship Management) software, on the other hand, focuses on managing and enhancing customer interactions and sales. While ERP manages resources and operations, CRM helps businesses build stronger customer relationships and drive revenue. Some business enterprises implement both to cover both operational and customer-focused needs.
Can small businesses benefit from enterprise software?
Yes, many types of enterprise software are now available in scalable versions suited for small businesses. Options like cloud-based ERP, CRM, and project management software provide small businesses and start-ups with affordable, flexible solutions without heavy infrastructure investment. These tools help small businesses manage resources, improve customer service, and optimize operations, leveling the playing field with larger competitors.
How does cloud-based enterprise software differ from on-premises software?
Cloud-based enterprise software is hosted on remote servers, making it accessible from anywhere with an internet connection. It typically operates on a subscription basis, reducing the need for in-house hardware and IT management. On-premises software, however, is installed directly on company servers, giving businesses full control over their data and system security. Cloud-based options offer flexibility and scalability, while on-premises solutions may appeal to businesses with specific security or compliance requirements.
What role does AI play in enterprise software?
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has significantly enhanced enterprise software applications, particularly in areas like data analytics, customer service, and automation. AI-powered tools can analyze vast data sets, generate predictive insights, and automate routine tasks. For instance, AI-driven chatbots in CRM software provide instant customer support, while AI in business intelligence (BI) software can forecast trends, empowering businesses to make proactive decisions.
Are there security risks associated with enterprise software?
While enterprise software offers robust functionality, it can introduce security risks, especially when dealing with sensitive data. Risks include data breaches, unauthorized access, and potential vulnerabilities in integrations. To mitigate these risks, businesses should choose software with strong encryption, multi-factor authentication, and regular security updates. Partnering with reputable data engineers and conducting regular audits is also key to maintaining data integrity and compliance.
How can enterprise software improve customer service?
Enterprise software enhances customer service by centralizing customer data and automating support workflows. Customer service software and CRM tools allow support teams to access detailed customer histories, ensuring faster and more personalized responses. Automated tools like AI-driven chatbots and knowledge bases also improve response times, while analytics can help identify common issues, allowing teams to proactively address customer needs.
What are the typical costs involved in implementing enterprise software?
Costs for enterprise software can vary widely based on the type, deployment (cloud-based or on-premises), and customization needs. Initial costs may include software licensing, setup fees, and training. Cloud-based solutions generally have lower upfront costs but require ongoing subscriptions, while on-premises software involves hardware and maintenance expenses. Additionally, consider long-term costs such as updates, integrations, and support, which are crucial for maximizing the software’s value.
What is the expected lifespan of an enterprise software solution?
The lifespan of enterprise software products varies, but a well-maintained solution can serve a business for 5 to 10 years or more. Cloud-based software often has continuous updates, ensuring functionality remains current. On-premises software may require periodic upgrades or replacements to stay compatible with evolving business needs and technology standards. Regular maintenance and scalability can help extend the lifespan, providing greater ROI over time.
Conclusion
Enterprise software has become a cornerstone for businesses seeking to optimize operations, enhance productivity, and stay competitive in a technology-driven landscape. From ERP systems that streamline core business functions to CRM tools that strengthen customer relationships, the right combination of enterprise software applications can transform the way an organization functions. As technology continues to advance, trends like AI integration, cloud-based solutions, and IoT connectivity are reshaping the potential of enterprise software, opening new avenues for innovation and efficiency.
Selecting the right types of enterprise software begins with understanding the unique needs of your business and evaluating software that aligns with your goals. Whether you’re a small business looking to improve efficiency or a large enterprise optimizing complex workflows, there’s a solution to support every aspect of your operations.
Investing in enterprise software solutions can be a significant decision, but the benefits of streamlined processes, data-driven decision-making, and improved customer satisfaction make it worthwhile. By staying informed about the latest trends and prioritizing software that offers flexibility and scalability, businesses can position themselves for long-term success in an evolving market.
 Derek Cohen
| Nov 7, 2024
Derek Cohen
| Nov 7, 2024
Analyzing business activities and data to formulate the best business development ideas is where I earn appreciations and remunerations. I’m an ardent reader, business adviser, gadget aficionado and an amateur yet an avid writer. My urge for innovative writing evokes every time I come across new gadgets, neo technology and novel technical events.